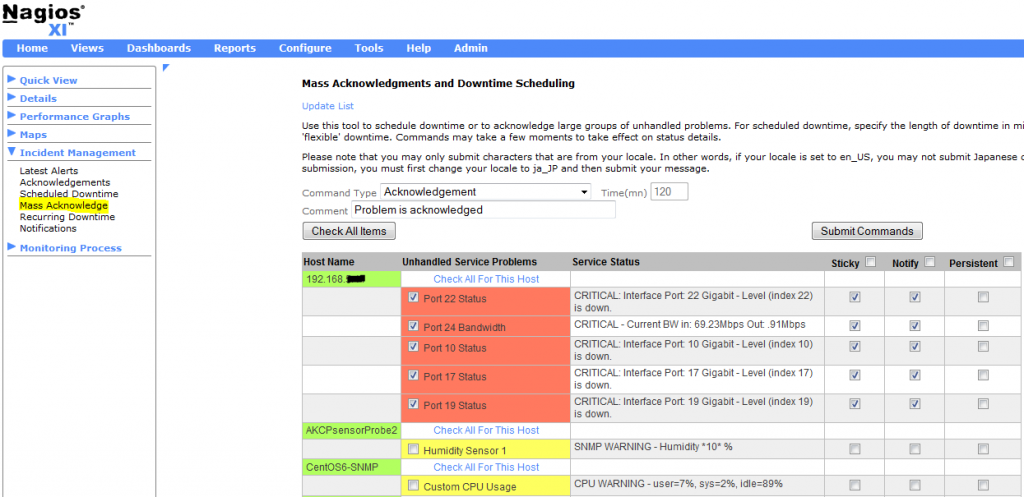
The Mass Acknowledge component in Nagios XI 2014 makes it very easy to mass acknowledge problems with hosts/services that are in non-OK state. The component allows you to suppress additional alerts to be sent out, while a team member works on resolving the issue(s). This component can also be used to schedule downtime for hosts/services, or schedule immediate checks in bulk.
From the Nagios XI Home page, navigate to Incident Management –> Mass Acknowledge. Select the function you would like to use from the Command Type drop-down menu. Then, select the hosts/services you wish to target. You can select some of the hosts/services by clicking on each checkbox or you can select all of them at once, by clicking on the Check All Items button. If you suspect that there are more hosts/services in a non-OK state than those you see on the page, you can always click on the Update List button on the top to update the list.
Next, set the length of downtime in minutes, and enter a comment. You have an option to choose whether to send or not to send alerts. Simply select or deselect the appropriate Notify checkboxes. Also, you have an option to make some (or all) of your comments Sticky or Persistent.
Note: If you want acknowledgement to disable notifications until the host/service recovers, check the Sticky acknowledgement checkbox. On the other hand, if you would like the host/service comment to remain once the acknowledgement is removed, check the Persistent acknowledgement checkbox.
Finally, click on the Submit Commands button.
Continue reading ‘Using the Mass Acknowledge Component in Nagios XI’